This week in AI brings a mix of strategic positioning, infrastructure planning, and new developer tools as the industry matures beyond the initial hype cycle. Microsoft AI is making bold claims about building a “humanist superintelligence” that keeps humans in control, while Wikipedia is dealing with the immediate consequences of AI training, watching its traffic decline as bots scrape content disguised as human visitors. Meanwhile, Canada is laying the groundwork for sovereign AI infrastructure with strategies expected next year, Google Maps is rolling out AI-powered building tools for developers, and xAI is preparing to showcase unreleased models at an upcoming hackathon. Here’s what happened.
Listen to the AI-Powered Audio Recap
This AI-generated podcast is based on our editor team’s AI This Week posts. We use advanced tools like Google NotebookLM, Descript, and Elevenlabs to turn written insights into an engaging audio experience. While the process is AI-assisted, our team ensures each episode meets our quality standards. We’d love your feedback—let us know how we can make it even better.
🇨🇦 Canadian Highlight: Policy & Regulation
Canada’s AI and Buy Canadian Strategies Expected to Roll Out in 2026
Canada’s AI minister, Evan Solomon, provided new details on the federal government’s plans for artificial intelligence infrastructure and domestic procurement policies, with both initiatives expected to launch next year.
Speaking at Toronto’s OneEleven innovation hub, Solomon discussed how the government plans to deploy nearly $926 million allocated in the 2025 budget for sovereign AI infrastructure, though $800 million of that funding carries over from the previous Liberal government’s compute strategy.
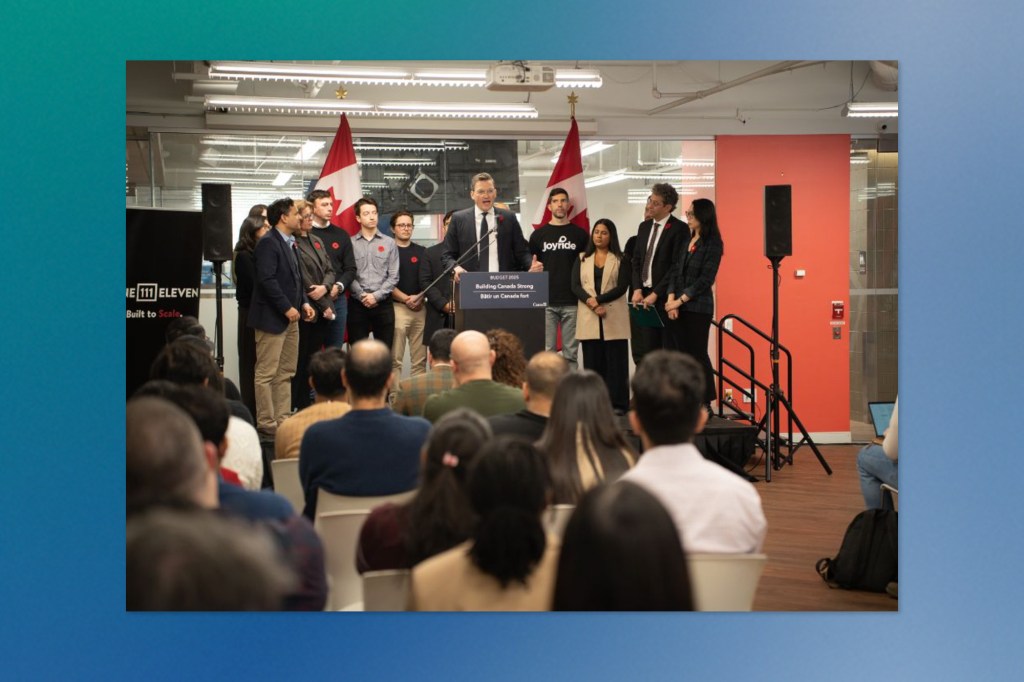

The minister indicated that Ottawa wants to address foundational issues before committing additional resources, particularly around building domestic data centers to handle Canada’s computing requirements. Solomon suggested the country’s forthcoming Defence Industrial Strategy will also factor into AI infrastructure planning.
A notable development is the government’s consideration of tying federal funding for AI and digital technologies to requirements that recipients purchase from Canadian suppliers. This approach would leverage procurement power to support domestic tech companies.
The AI Task Force, assembled this fall to inform the government’s strategy, has completed its initial work and delivered recommendations following a 30-day consultation period. Solomon said the government received 28 submissions from task force members, along with 11,000 public responses, a record for the department. Officials are using AI tools to process the public feedback.
The minister is meeting with task force members over the coming weeks to consolidate their input before finalizing the strategy. He confirmed the government is exploring various mechanisms to encourage data center construction, including potential financial guarantees or agreements to purchase computing capacity.
Separately, Canada’s Buy Canadian Policy received nearly $186 million over five years in the budget. The policy begins rolling out this month for defence and construction procurement, with full implementation across government purchases planned for spring 2026.
Solomon emphasized that while the government will play an enabling role, he expects the private sector to handle much of the AI infrastructure development independently. “We’re not here to be backstopping everybody,” he said.
💡 Strategy & Vision
Microsoft AI Announces New Push for “Humanist Superintelligence”
Microsoft AI has unveiled plans to develop what it calls “humanist superintelligence” through a newly formed team, pledging to keep human interests at the forefront of advanced AI development.
In a recently published blog post, Microsoft AI chief Mustafa Suleyman introduced the concept as a counterpoint to concerns about uncontrolled AI systems. Rather than pursuing artificial general intelligence without boundaries, Suleyman’s vision centers on creating highly capable AI that remains “carefully calibrated, contextualized, within limits” and specifically designed to tackle concrete human problems.
The announcement comes as Microsoft’s relationship with OpenAI enters a new phase. Recent changes to their partnership now allow Microsoft to pursue AGI development independently or with other partners, potentially creating competition between the two companies despite their close collaboration.
Suleyman outlined three primary focus areas for this humanist approach: AI companions that assist with learning and productivity while supporting rather than replacing human connection; medical AI systems that could bring expert-level diagnostics to healthcare settings worldwide; and AI-driven breakthroughs in clean energy production and storage.
The Microsoft AI leader emphasized that his team rejects framing AI development as a race, instead positioning it as a long-term effort to deliver tangible benefits. “Humans matter more than AI,” Suleyman wrote, describing the goal as creating subordinate, controllable systems that keep humanity firmly in control rather than opening what he called a “Pandora’s Box” of unpredictable consequences.
⚙️ Model Updates
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.1 with Warmer Tone and Adaptive Reasoning
OpenAI is rolling out GPT-5.1, upgrading both its most-used model and its advanced reasoning variant with improvements focused on conversational quality and intelligence.
GPT-5.1 Instant, ChatGPT’s default model, now features a warmer and more conversational tone by default while maintaining clarity and usefulness. The model also includes improved instruction-following capabilities, answering specific questions users ask more reliably rather than providing tangential information.
For the first time, GPT-5.1 Instant can use adaptive reasoning, allowing it to decide when to think before responding to challenging questions. This results in more thorough and accurate answers to complex queries while maintaining fast response times for simpler questions, reflected in significant improvements on math and coding benchmarks such as AIME 2025 and Codeforces.
GPT-5.1 Thinking, the advanced reasoning model, now adapts its thinking time more dynamically, spending less time on straightforward tasks and more time on complex problems. The updated model is roughly twice as fast on simple queries and twice as thorough on difficult ones compared to its predecessor.
The model also produces clearer responses with less jargon and fewer undefined terms, making OpenAI’s most capable model more approachable for complex work tasks and technical explanations. The default tone is also warmer and more empathetic across both variants.
Alongside the model improvements, OpenAI expanded ChatGPT’s customization options with new personality presets, including Professional, Candid, and Quirky, joining the existing Default, Friendly, and Efficient options. Users can also experiment with granular controls over characteristics like conciseness, warmth, and emoji usage. ChatGPT can now proactively suggest updating these preferences during conversations when it detects a user requesting a particular tone.
The updates are rolling out starting today to paid subscribers (Pro, Plus, Go, Business) before expanding to free users. GPT-5.1 Instant and Thinking will arrive in the API later this week. Legacy GPT-5 models will remain available for three months to allow users time to compare and adapt. Enterprise and Edu customers receive a toggle for 7 days of early access.
OpenAI noted the “5.1” designation reflects meaningful improvements while remaining within the GPT-5 generation, with future iterative upgrades following the same naming pattern.
🌐 Platform & Ecosystem
Wikipedia Pushes AI Companies Toward Paid API Instead of Scraping
Wikipedia is making a direct appeal to artificial intelligence companies: pay for authorized access to its content rather than scraping the site and straining its infrastructure.
In a blog post published Monday, the Wikimedia Foundation outlined guidelines for AI developers, emphasizing that companies should access Wikipedia’s material through Wikimedia Enterprise, its commercial API platform. The paid service enables organizations to use Wikipedia content at scale without overwhelming the site’s servers, while subscription revenue supports the nonprofit’s operations.
The organization stopped short of threatening legal consequences for unauthorized scraping, but the message comes as Wikipedia grapples with the impact of AI bots on its traffic patterns. After upgrading its detection systems, Wikipedia discovered that unusually high traffic levels during May and June stemmed from AI bots attempting to disguise themselves as human visitors. During the same period, actual human pageviews dropped 8% compared to the previous year.
The decline in legitimate traffic raises concerns about Wikipedia’s sustainability model, which depends on both volunteer contributors and individual donations. The Wikimedia Foundation warned that reduced visibility could mean fewer people joining as editors to expand and maintain content, as well as fewer donors supporting the platform financially.
Beyond the technical access question, Wikipedia stressed the importance of attribution. The foundation called on generative AI developers to clearly credit the human volunteers whose work feeds AI training and outputs, arguing that transparency about information sources builds trust and encourages people to engage with original sources.
Earlier this year, Wikipedia released its own AI strategy focused on using the technology to assist editors with repetitive tasks and translation work, positioning AI as a tool to support rather than replace human contributors.
🛠️ Developer Tools & Products
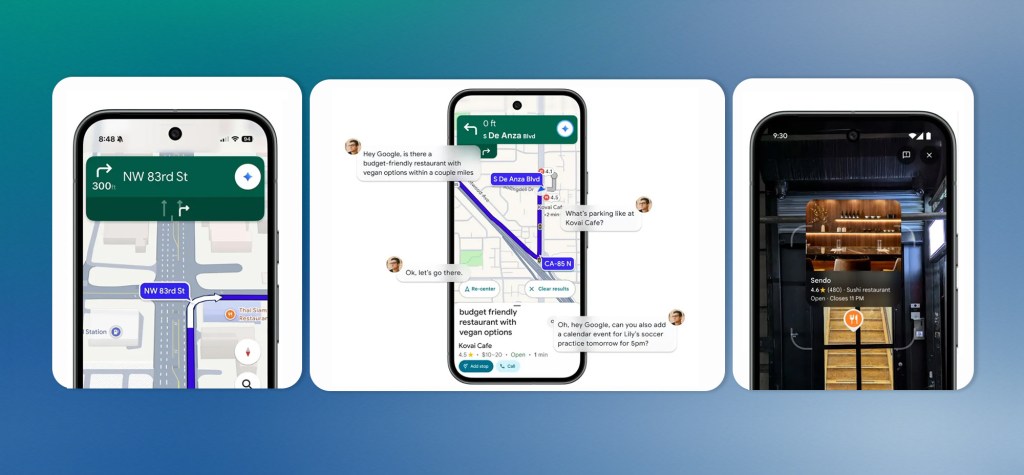
Google Maps Introduces AI-Powered Development Tools for Interactive Projects
Google Maps is rolling out a suite of AI-driven features designed to help developers and users build interactive mapping applications more easily, with all tools powered by the company’s Gemini models.
The centrepiece is a builder agent that functions similarly to AI coding assistants, allowing users to describe map-based projects in plain language and generate the corresponding code. Developers can request features such as Street View city tours, real-time weather visualization maps, or listings of pet-friendly hotels, and the tool produces working prototypes. Generated code can be exported, tested with personal API keys, or further refined in Firebase Studio.
Google is also launching a styling agent within the same toolset for companies wanting maps that align with their visual identity, enabling users to customize map appearances to match specific themes or brand colour schemes.
On the data integration front, Google introduced Grounding Lite, which leverages the Model Context Protocol (MCP) standard to let developers connect their own AI models to Google Maps data. This allows AI assistants to answer location-based queries, such as finding the nearest grocery store. Accompanying this is Contextual View, a low-code Maps component that can visually display answers as lists, map views, or 3D representations.
For technical support, Google added an MCP server that connects directly to Google Maps documentation, giving developers AI-assisted access to information about using the Maps API. This follows last month’s launch of extensions for Gemini’s command line tool that provide Maps data access.
xAI Announces 24-Hour Hackathon with Early Access to Unreleased Models
xAI is hosting a 24-hour hackathon in the San Francisco Bay Area on December 6-7, offering developers an exclusive first look at experimental models and new coding capabilities.
The event runs continuously from 4 PM Saturday through 4 PM Sunday, bringing together developers and engineers to build applications with unreleased Grok models and X API tools not yet available to the public. xAI is providing full support for the around-the-clock session, including sleeping bags, large screens, food, coffee, and energy drinks. The top five projects will be featured on xAI’s official X account, while the top three teams will receive special awards. Registration closes November 22, with applications reviewed on a rolling basis.
The hackathon coincides with speculation about new Grok model releases, potentially versions 4.1, 4.2, or another iteration, though xAI hasn’t confirmed specific version numbers. Participants will gain hands-on experience with these experimental models before their broader launch.

Beyond model updates, development traces reveal xAI is building “Grok Code Remote,” a cloud-based code execution feature that would let users run code in remote environments directly from the web. The tool appears designed to compete with similar offerings from OpenAI and Anthropic, with planned integrations including GitHub repository access and automated pull request creation.
Early indicators also suggest xAI may be developing a “local” variant of Grok Code, though its exact purpose remains unclear. Current evidence points toward it being aimed at internal development work or advanced developer use cases rather than widespread consumer deployment, though speculation exists around a potential desktop application.
The hackathon represents xAI’s push to build developer engagement and establish itself in the competitive AI coding tools market. More details about the new models and code execution features are expected to emerge as participants test the unreleased technology during the December event.
Keep ahead of the curve – join our community today!
Follow us for the latest discoveries, innovations, and discussions that shape the world of artificial intelligence.