The AI wars escalated to new heights this week as tech titans placed massive bets on fundamentally different visions of the future of artificial intelligence. While Meta went all-in on “superintelligence” with a staggering $14.3 billion acquisition, Google quietly revolutionized education by embedding AI tutors into every classroom. But perhaps the most sobering development came from new research revealing a stark reality: the AI revolution is creating clear winners and losers, with strategic adopters pulling so far ahead that late movers may never catch up. Welcome to the week AI adoption became an existential business imperative.
Listen to the AI-Powered Audio Recap
This AI-generated podcast is based on our editor team’s AI This Week posts. We use advanced tools like Google Notebook LM, Descript, and Elevenlabs to turn written insights into an engaging audio experience. While the process is AI-assisted, our team ensures each episode meets our quality standards. We’d love your feedback—let us know how we can make it even better.
Meta Assembles Its “Superintelligence” Dream Team
Mark Zuckerberg is making his biggest bet yet in the AI race, and he’s not holding back. This week, Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg officially announced the formation of Meta Superintelligence Labs (MSL), a new division that consolidates all of the company’s AI efforts under one ambitious umbrella. The move comes as Zuckerberg declared that “developing superintelligence is coming into sight” and positioned Meta to “lead the way” in what he calls “the beginning of a new era for humanity.”
The centrepiece of this strategy is 28-year-old Alexandr Wang, the MIT dropout who built Scale AI into a $29 billion data labelling powerhouse before Meta acquired a 49% stake for $14.3 billion. Wang now takes on the newly created role of Chief AI Officer at Meta, making this the company’s second-largest acquisition ever after WhatsApp.
But Wang isn’t coming alone. Former GitHub CEO Nat Friedman will partner with Wang to help lead the division, and Meta has been aggressively poaching talent from OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Anthropic, with recent hires including four Chinese researchers from OpenAI. The talent war has reached unprecedented levels, with reports indicating that Meta is offering bonuses of up to $100 million to entice engineers to switch companies.
This reorganization signals Meta’s acknowledgment that it has fallen behind in the AI race. The company’s Llama 4 release in April faced criticism for inflated performance metrics and failing to keep pace with competitors, such as China’s DeepSeek. Now, Zuckerberg is betting that Wang’s business acumen and talent acquisition skills can turn things around.
The stakes couldn’t be higher. Meta Superintelligence Labs will house everything from the open-source Llama models to the company’s Fundamental AI Research projects, all while pursuing the holy grail of artificial general intelligence. As Zuckerberg put it in his internal memo: “Meta is uniquely positioned to deliver superintelligence to the world,” thanks to its strong business model, experience serving billions of users, and leadership in AI glasses and wearables.
Google Brings AI Tutors to Every Classroom
While Meta chases superintelligence, Google is taking a different approach: embedding AI directly into the fabric of education. At this week’s ISTE conference, the tech giant unveiled an ambitious suite of AI tools designed to transform how teachers teach and students learn, marking one of the most comprehensive AI pushes into education to date.
At the heart of this initiative is Gemini for Education, a specialized version of Google’s AI assistant built specifically for schools. Unlike the consumer version, this educational variant runs on the more powerful Gemini 2.5 Pro model, which offers significantly higher usage limits, enterprise-grade data protection, and administrative controls—all available free to schools using Google Workspace for Education.
But Google’s education play goes far beyond just another chatbot. The company is rolling out Gemini in Classroom, a collection of over 30 AI-powered tools that automate the mundane tasks that consume teachers’ time. These range from generating vocabulary lists with definitions to creating personalized lesson plans and even crafting quizzes from uploaded documents. Teachers can now ask AI to brainstorm real-world examples that will resonate with their specific grade level, turning curriculum planning from hours of work into minutes of conversation.
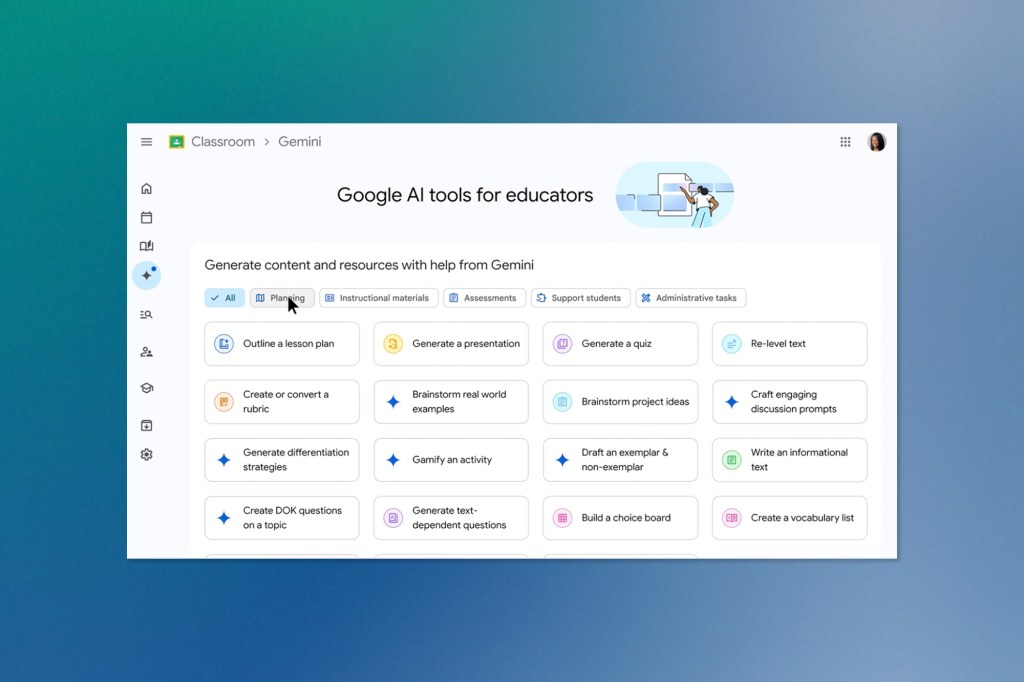
Perhaps most intriguingly, Google is introducing “Gems”—custom AI experts that teachers can create and eventually share with colleagues. Think of them as specialized tutors trained on specific course materials, designed to provide consistent, curriculum-aligned support to students who need extra help or want to dive deeper into a subject.
The timing is crucial. Schools are grappling with an uncomfortable reality: students are already using AI for homework help, often turning to ChatGPT before asking their teachers. Rather than fight this trend, Google is offering to channel it through education-friendly tools with proper safeguards and teacher oversight.
Students themselves get access to personalized quiz generation through Gemini Canvas, allowing them to create practice tests on any subject. Meanwhile, NotebookLM is expanding to younger students, complete with new Video Overviews that can transform study materials into engaging educational videos.
Google is also tackling the practical side of classroom management with new Class tools for managed Chromebooks. Teachers can now broadcast content directly to student screens, share resources through a digital workbook system, and even restrict browsing to keep students focused during lessons.
The education sector’s embrace of AI represents a fascinating contradiction: the same technology that terrifies educators due to concerns about cheating is being positioned as the solution to personalized learning. Google’s strategy is working with this tension rather than against it, providing tools that enhance rather than replace human instruction while maintaining the oversight and control that schools desperately need.
Cursor Takes AI Coding Agents Mobile
The battle for developer mindshare is heating up, and Cursor just made a bold move to stay ahead of the pack. Anysphere, the company behind the viral AI coding editor, has launched a comprehensive web application that brings its autonomous coding agents to any browser—desktop or mobile—marking a significant evolution beyond its traditional IDE-based approach.
This isn’t just another product launch; it’s a strategic expansion that transforms how developers interact with AI throughout their entire workflow. The new web platform allows developers to assign complex coding tasks using natural language, monitor multiple agents simultaneously, and seamlessly merge completed work back into their codebase—all from wherever they happen to be.
The timing couldn’t be better for Anysphere. The company recently announced that Cursor has surpassed $500 million in annualized recurring revenue, with more than half of the Fortune 500 companies now utilizing the platform, including tech giants such as Nvidia, Uber, and Adobe. To capitalize on this momentum, they’ve also introduced a premium $200-per-month Pro tier alongside their existing $20 monthly plan.
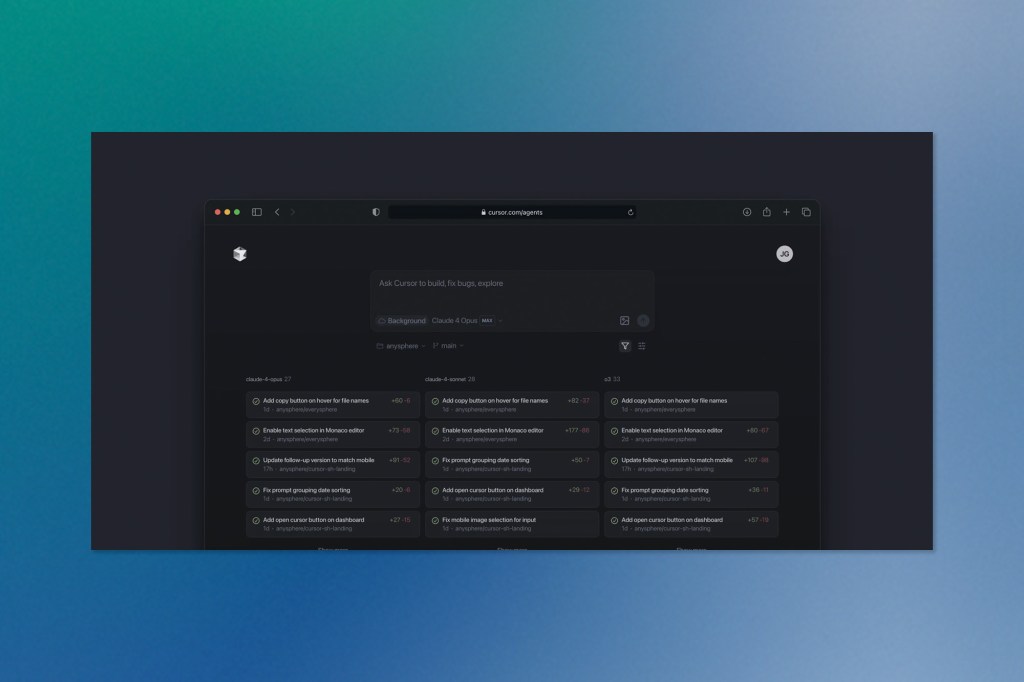
What sets Cursor apart from the crowded field of AI coding tools is its deliberate approach to agent deployment. Rather than rushing out “demo-ware” that looks impressive but fails in practice—a criticism levelled at many early AI coding agents—Anysphere has taken a measured approach. Their background agents, first launched in May, are designed to handle autonomous coding tasks while maintaining seamless handoffs to human developers when needed.
The web app represents the culmination of a multi-platform strategy that began with Slack integration in June, allowing teams to assign tasks by simply tagging “@Cursor” in conversations. Now, with mobile and web access, developers can initiate work from their phones, monitor progress during commutes, and transition back to their full IDE for detailed refinements.
This workflow-first philosophy distinguishes Cursor from competitors who’ve focused on full automation. Each agent generates a unique shareable link, making collaboration as simple as sharing a Google Doc. Teams can track multiple agents working on different features simultaneously, creating a new paradigm where AI becomes an ambient part of the development process rather than a siloed tool.
CEO Michael Truell’s prediction that AI coding agents will handle at least 20% of software engineering work by 2026 seems less ambitious and more inevitable when you can spin up coding assistants from anywhere, at any time. The question isn’t whether AI will transform software development—it’s whether traditional development tools can keep pace with this new reality.
Thomson Reuters Study Exposes Massive AI Strategy Divide
Thomson Reuters’ 2025 Future of Professionals report reveals that the professional services industry is fracturing into two distinct camps: strategic AI adopters who are reaping substantial returns, and those who risk being left behind. The comprehensive study, surveying 2,275 global professionals across legal, risk, compliance, tax, accounting, audit, and global trade sectors, paints a stark picture of opportunity and peril in equal measure.
The research, conducted in February and March 2025 across North America, Latin America, the UK, Europe, and the APAC region, uncovers what researchers describe as “the jagged edge” of AI adoption. While 40% of organizations are implementing AI without a coherent strategy, those with a visible, defined approach are dramatically outperforming their peers. Organizations with formal AI strategies are twice as likely to experience revenue growth directly attributed to AI implementation and 3.5 times more likely to achieve critical AI benefits compared to those with no significant adoption plans.
The study’s most striking finding centers on a massive missed opportunity. Despite clear evidence that strategic AI adoption drives measurable business results, only 22% of organizations have established visible AI strategies. This leaves the vast majority scrambling with ad hoc implementations while missing out on transformative returns.
The financial implications are staggering. The research predicts professionals will save an average of five hours weekly through AI usage—a significant increase from the four hours forecasted in 2024. When scaled across the U.S. market, these efficiency gains translate to an estimated $20 billion annual impact for the legal industry and $12 billion for the CPA sector, representing an average annual value of $19,000 per professional.
What makes this divide particularly concerning is the emergence of what researchers refer to as an “implementation reality gap.” While 80% of professionals believe AI will have a transformational impact on their work over the next five years, only 38% expect significant change at their organizations this year. This disconnect reveals a fundamental challenge: widespread enthusiasm for AI doesn’t automatically translate into effective deployment.
The study identifies three critical success factors that separate AI leaders from laggards. First, individual professionals need robust AI knowledge and empowerment—those with a good or expert understanding of AI are 2.8 times more likely to see organizational benefits. Second, organizations must fundamentally adapt their workflows and processes, with one-third having already experienced team workflow changes in the past year. Finally, leadership must actively invest in AI technology while modelling new behaviours during transformation periods.
To access the full report, visit https://www.thomsonreuters.com/en/c/future-of-professionals
Keep ahead of the curve – join our community today!
Follow us for the latest discoveries, innovations, and discussions that shape the world of artificial intelligence.