The AI industry continues its rapid expansion into everyday tools and transactions, but this week’s developments reveal both the technology’s growing utility and its persistent challenges. OpenAI and PayPal are pushing AI deeper into consumer commerce with in-chat shopping capabilities, while Adobe is betting big on AI-powered creativity with new assistants and orchestration tools across its platform. At the same time, OpenAI disclosed that over a million people weekly discuss suicide with ChatGPT, prompting major safety upgrades developed with mental health experts. Meanwhile, a comprehensive study found that nearly half of AI assistant responses to news questions contain significant errors, raising concerns about information integrity. As Canada’s new AI minister signals forthcoming legislation, the tension between innovation and regulation remains front and center, with experts warning that without robust safeguards, the technology risks undermining both individual well-being and democratic participation.
Listen to the AI-Powered Audio Recap
This AI-generated podcast is based on our editor team’s AI This Week posts. We use advanced tools like Google NotebookLM, Descript, and Elevenlabs to turn written insights into an engaging audio experience. While the process is AI-assisted, our team ensures each episode meets our quality standards. We’d love your feedback—let us know how we can make it even better.
🇨🇦 Canadian Highlight: Policy & Regulation
Canada’s AI Minister Signals New Legislation as Experts Push for Stronger Rules
Canada’s newly appointed AI and digital innovation minister, Evan Solomon, is preparing to introduce new legislation targeting artificial intelligence and data privacy, with a particular focus on deepfakes and data-handling practices. Speaking at the Attention: Govern or Be Governed Conference in Montreal, Solomon outlined plans to address data transfer protocols, chain-of-custody requirements, and protections for children’s sensitive information.
The legislative push comes after the previous government’s Artificial Intelligence and Data Act, part of Bill C-27, died when Parliament was prorogued in January. While Solomon has stated he won’t resurrect that specific bill, certain elements may be incorporated into new proposals. He’s emphasized a “light, tight, right” regulatory philosophy aimed at avoiding restrictions that could hamper Canadian innovation, with priorities including scaling AI companies, driving adoption, building trust, and developing sovereign AI infrastructure.
Solomon’s department has launched a 30-day task force sprint involving industry leaders and researchers to help shape Canada’s refreshed AI strategy, which could debut by late 2025 or early 2026. Over 6,500 individuals have reportedly contributed to online consultations on the strategy.
However, Solomon’s cautious regulatory stance drew contrast from other speakers at the conference. European Union Commissioner Michael McGrath argued that robust rules actually enable innovation rather than constrain it, citing the EU’s Digital Services Act and AI Act as examples. Privacy Commissioner Philippe Dufresne urged Canada to match its international partners in enforcement capabilities, calling it “low-hanging fruit” that would level the global playing field.
AI pioneer Yoshua Bengio went further, advocating for international treaties rather than just domestic regulation. He warned that without coordinated action among middle-power nations, countries like Canada risk being dominated by AI superpowers like the United States and China. Bengio recently co-signed an open letter calling for a ban on the development of AI superintelligence.
🎨 Creative Tools & Product Launches
Adobe Unveils AI Assistants for Express and Photoshop, Plus Major Firefly Updates
Adobe rolled out a comprehensive suite of AI enhancements across its creative platform, introducing new assistants for Express and Photoshop, launching Firefly Image 5, and previewing Project Moonlight, which is an orchestration agent designed to coordinate across multiple Adobe apps and social channels.
For Adobe Express, the company created an entirely new assistant mode rather than the typical sidebar approach. Users can toggle between AI prompt mode for generating images and designs, then switch back to traditional editing tools. Alexandru Costin, Adobe’s VP of generative AI, explained that the dual-mode strategy targets students and professionals, allowing them to get “the best of both worlds” with both accessibility and control.

The Photoshop assistant, currently in closed beta, takes the sidebar approach and can understand different layers, automatically select objects, create masks, and handle repetitive tasks like background removal or colour adjustments.
Adobe also launched Firefly Image 5, bringing substantial improvements over its predecessor. The new model generates images natively at up to 4 megapixels and delivers better human rendering. A standout feature treats different objects as editable layers, allowing prompt-based adjustments while preserving image integrity. Users can resize, rotate, and modify individual elements without compromising overall quality.
In a significant expansion, Firefly now supports custom model creation through a closed beta feature. Creators can drag and drop their own images, illustrations, and sketches to build personalized image models reflecting their unique style. The platform already offered third-party models from OpenAI, Google, Runway, Topaz, and others; custom models take personalization further.
The redesigned Firefly website consolidates functions into a unified prompt box for switching between image and video generation, selecting AI models, and adjusting aspect ratios. The homepage now displays user files and recent generation history with quick shortcuts to other Adobe applications.
Audio capabilities expanded through partnerships with ElevenLabs, enabling AI-generated soundtracks and speech for videos. A new prompt-building interface using word cloud selection simplifies the creative process.
Project Moonlight represents Adobe’s most ambitious AI initiative. It’s an orchestration assistant that functions as a creative director across multiple Adobe tools and social platforms. The agent connects to Creative Cloud libraries and social accounts to understand a user’s style, then coordinates with specialized assistants in Photoshop, Premiere, and Lightroom to execute creative visions.
Moonlight analyzes social media performance, identifies trends, and crafts content strategies while generating images, videos, and posts that match a creator’s authentic voice. The product is in early private beta, with broader access planned for the coming months.
Adobe is also integrating Express with ChatGPT through OpenAI’s app integrations API, allowing design creation directly within ChatGPT conversations.
Across Creative Cloud, Adobe added third-party model options, including Google’s Gemini 2.5 Flash and Black Forest Labs’ FLUX.1 Kontext, for Photoshop’s generative fill feature. Premiere Pro gains an AI-powered object mask for easy identification and selection of subjects for effects and colour adjustments.
Costin characterized Firefly’s target audience as “next-generation creative professionals” who are “GenAI-oriented” and integrate AI throughout their workflows. The standalone Firefly platform gives Adobe flexibility to experiment with interfaces without disrupting the muscle memory of professionals accustomed to established Creative Cloud workflows, positioning the company to compete with rivals like Canva as AI reshapes creative tools.
🛒 AI-Powered Commerce
PayPal and OpenAI Team Up for In-Chat Shopping
PayPal is making a significant move into AI-powered commerce by partnering with OpenAI to enable purchases directly within ChatGPT starting in 2026. The payment giant is implementing OpenAI’s Agentic Commerce Protocol, an open-source framework that allows businesses to list their products within AI applications, alongside OpenAI’s Instant Checkout capability, which debuted in September.
The integration means ChatGPT users will be able to complete entire transactions without ever leaving their conversation, using their PayPal accounts to handle payments. PayPal will provide its standard buyer and seller protections along with dispute resolution services, and will also process credit card payments through a dedicated API.
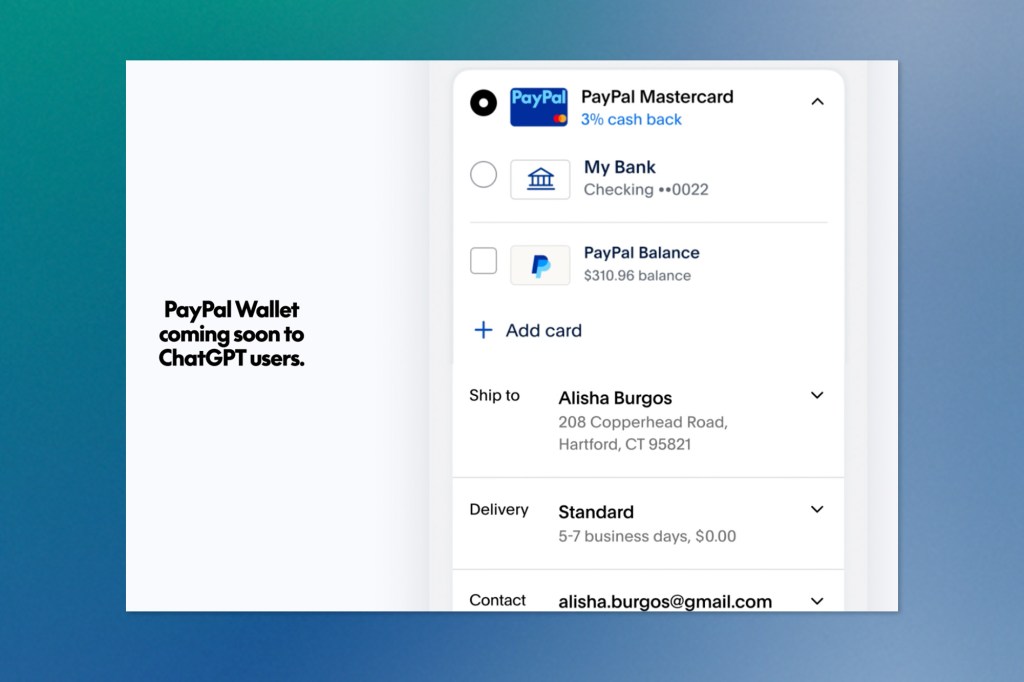
For merchants using PayPal’s platform, the rollout begins with products in apparel, fashion, beauty, home improvement, and electronics becoming searchable within ChatGPT. The setup requires zero effort from individual sellers. PayPal manages all the technical routing and payment processing automatically.
This isn’t PayPal’s first venture into AI-enabled shopping. Earlier this year, the company integrated with Perplexity’s AI search platform, and in September, adopted Google’s Agent Payments Protocol for use across Google’s ecosystem. The company is also launching an agentic commerce suite to help merchants distribute their catalogues across multiple AI platforms while gathering behavioural insights.
Beyond commerce, PayPal is deploying ChatGPT enterprise-wide for its workforce and giving engineers access to OpenAI’s development tools.
⚠️ Safety & Accuracy Concerns
Study Finds 45% of AI Assistant News Responses Contain Significant Issues
AI assistants struggle substantially with accuracy when answering news-related questions, according to research from the European Broadcasting Union and BBC that evaluated 2,709 responses across leading platforms.
The study examined free consumer versions of ChatGPT, Copilot, Gemini, and Perplexity answering news questions in 14 languages across 22 public-service media organizations spanning 18 countries. Overall, 45% of responses contained at least one significant problem, while 81% had some form of issue.
Sourcing emerged as the primary weakness, affecting 31% of responses at a significant level. Problems included missing citations, misattributed sources, and misleading references that didn’t support the claims being made.
Google Gemini performed notably worse than competitors, with 76% of its responses containing significant problems, largely driven by sourcing issues present in 72% of responses. The other three assistants showed major problems in 37% or fewer responses, with sourcing issues below 25%.
Accuracy errors also appeared frequently. Multiple assistants incorrectly identified Pope Francis as the current Pope in late May responses, despite his death in April. Gemini mischaracterized legal changes regarding disposable vapes in one instance.
The research team generated responses between late May and early June using 30 standardized core questions plus optional localized queries. Participating organizations temporarily removed technical blocks that normally restrict AI assistant access to their content during the testing period, then reinstated them afterward.
The EBU warned that AI’s distortion of news content appears consistent across languages and territories, suggesting systemic rather than isolated problems. The organization released a News Integrity in AI Assistants Toolkit alongside the findings, providing guidance for technology companies, media organizations, and researchers.
EBU Media Director Jean Philip De Tender emphasized the democratic stakes, noting that when people cannot determine what information to trust, they often stop trusting anything, potentially deterring civic participation.
The findings highlight risks both for users relying on AI assistants for news research and for publishers whose content may be misrepresented in AI-generated summaries, even when properly cited.
OpenAI Upgrades ChatGPT’s Mental Health Responses After Working with 170+ Experts
OpenAI announced Monday it has significantly improved how ChatGPT handles sensitive mental health conversations, working with over 170 clinical mental health professionals to develop better detection and response systems. The updates come as the company revealed that approximately 0.15% of ChatGPT’s weekly active users, translating to more than a million people, given its 800 million weekly user base, engage in conversations containing explicit indicators of suicidal planning or intent.
The company disclosed additional concerning patterns: around 0.15% of weekly users show heightened emotional attachment to ChatGPT, while roughly 0.07% display possible signs of mental health emergencies related to psychosis or mania. OpenAI characterized these conversations as “extremely rare” but acknowledged they affect hundreds of thousands of individuals each week.
The improvements focus on three priority areas: mental health emergencies like psychosis and mania, self-harm and suicide risk, and unhealthy emotional dependency on AI. OpenAI’s updated GPT-5 model now reduces problematic responses by 65-80% across these categories compared to earlier versions.
The company followed a structured five-step development process: defining specific harms, measuring their occurrence through real-world data and evaluations, validating approaches with external experts, implementing mitigations through model training and product modifications, and continuously measuring effectiveness. Central to this work were detailed taxonomies, essentially guidebooks describing what appropriate and inappropriate model behaviours look like in sensitive situations.
Performance improvements have been substantial. In evaluations of challenging mental health conversations involving psychosis or mania, the new GPT-5 model achieved 92% compliance with OpenAI’s safety standards, up from just 27% in the previous version. For suicide and self-harm scenarios, compliance rose from 77% to 91%. The most dramatic gains appeared in emotional reliance conversations, where compliance jumped from 50% to 97%.
The model was specifically trained to avoid reinforcing delusional beliefs while responding empathetically, encourage real-world relationships over AI dependency, recognize indirect distress signals, and maintain safety standards throughout extended conversations, previously a weak point where safeguards would degrade over time. OpenAI’s testing shows the latest model maintains over 95% reliability even in lengthy exchanges specifically designed to be challenging.
Beyond model training, OpenAI implemented product-level changes, including expanded crisis hotline access, automatic routing of sensitive conversations from less-safe models to more capable ones, and gentle prompts encouraging users to take breaks during prolonged sessions. The company is also developing age-detection technology to automatically identify children and enforce stricter protections, alongside enhanced parental controls.
These updates have been added to OpenAI’s Model Spec, which is the company’s guiding document for AI behaviour, making explicit that models should support real-world relationships, avoid affirming ungrounded beliefs related to mental distress, and pay attention to subtle warning signs.
The mental health improvements carry particular urgency for OpenAI, which faces a lawsuit from parents whose teenage son discussed suicidal thoughts with ChatGPT before taking his own life. State attorneys general from California and Delaware have also warned the company about protecting young users. These concerns could impact OpenAI’s planned corporate restructuring.
Despite the progress, gaps remain. A portion of responses still fall short of OpenAI’s standards, and older models like GPT-4o, which performed significantly worse in safety evaluations, remain available to millions of paying subscribers.
Keep ahead of the curve – join our community today!
Follow us for the latest discoveries, innovations, and discussions that shape the world of artificial intelligence.