From Seoul to Silicon Valley, AI innovation continues to accelerate. This week’s highlights include Canadian company Cohere’s expansion into South Korea, signalling its global enterprise ambitions, and the rise of AI-powered browsers that aim to simplify task automation. Netflix openly embraces generative AI for visual effects, while Reflection, a new startup founded by former DeepMind researchers, introduces an AI agent focused on code comprehension. Meanwhile, Google enters the “vibe-coding” space with Opal, a visual app-building tool for non-programmers. Plus, a new study reveals how AI companions are quietly becoming part of daily life for American teens.
Listen to the AI-Powered Audio Recap
This AI-generated podcast is based on our editor team’s AI This Week posts. We use advanced tools like Google Notebook LM, Descript, and Elevenlabs to turn written insights into an engaging audio experience. While the process is AI-assisted, our team ensures each episode meets our quality standards. We’d love your feedback—let us know how we can make it even better.
Canadian AI Innovation
Cohere Expands Asian Operations with Seoul Office
Toronto-based Cohere is positioning itself as a major player in the global enterprise AI market by establishing Seoul, South Korea, as its Asia-Pacific headquarters, marking a significant milestone for the Canadian startup’s international ambitions.
The company has appointed Andrew Chang, an executive with extensive experience at Google Cloud, Microsoft, IBM, and Samsung SDS, to lead the region as VP of APAC. Chang most recently served as Area Vice President and Country Manager for Confluent, a data platform in Korea, bringing deep knowledge of the South Korean technology landscape to Cohere’s expansion efforts.
CEO and co-founder Aidan Gomez highlighted South Korea’s strategic importance, citing the country’s “vibrant AI ecosystem” and growing demand for sovereign AI solutions. The Seoul office will serve as Cohere’s central hub for driving business growth across the Asia-Pacific region, with immediate plans to hire key personnel and accelerate the adoption of the company’s multilingual AI platforms.

Cohere’s expansion builds on successful partnerships with major South Korean enterprises, particularly LG CNS, with whom they’ve developed AI solutions for both private sector clients and government agencies. Their collaboration includes an “intelligent AI diplomatic security data platform” for South Korea’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs, demonstrating Cohere’s ability to handle sensitive government applications with their security-first approach.
The Canadian company is targeting regulated industries including finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and energy sectors, where its focus on secure, multilingual AI solutions addresses critical data sensitivity requirements. Alongside the commercial expansion, Cohere Labs is launching a research grant program in South Korea to collaborate with academic institutions on AI safety and multilingual capabilities.
This Seoul expansion follows Cohere’s recent opening of its Montreal office and represents another step in the company’s global growth strategy, following its $500 million Series D funding round at a $5.5 billion valuation, with Japanese IT services firm Fujitsu among the investors.
AI Browsers Add Skill Sharing and Task Automation
AI-powered browsers are taking steps to bridge the gap between their ambitious promises and current capabilities by introducing features that make repetitive tasks more accessible to users.
The Browser Company launched version 0.1 of a skill gallery for its Dia browser, formalizing user-shared prompts and commands into categorized skills. This gallery lets users integrate prompts into personal libraries, enabling actions via natural language, like finding local events or generating code, which can be saved for future use as shortcuts.
Meanwhile, Perplexity is preparing similar functionality for its Comet browser. CEO Aravind Srinivas announced plans to introduce pre-built shortcuts for common workflows, including tab organization, meeting preparation, and social media trend monitoring. The browser will also support user-created automation scripts through natural language prompts, drawing comparisons to Tampermonkey’s browser extension capabilities but with a more accessible interface.
While these skill galleries won’t solve the fundamental challenges of complex task automation, they offer a more pragmatic path forward, turning AI browsers into platforms where useful workflows can be discovered, shared, and refined by their user communities.
Netflix Openly Uses AI for Visual Effects in Original Content
Netflix has crossed a significant threshold by publicly acknowledging its use of generative AI to create visual effects in one of its original productions, marking a notable shift in how streaming platforms approach content creation costs.
During a recent earnings call, Netflix co-CEO Ted Sarandos revealed that the production team behind the sci-fi series “The Eternaut” used AI to generate a building collapse scene set in Buenos Aires. According to Sarandos, this AI-generated sequence was completed ten times faster than traditional VFX methods would have allowed, while also making the scene financially viable within the show’s budget constraints.

The disclosure marks Netflix’s first public acknowledgment of utilizing generative AI for visual effects in its original programming, signalling a broader industry trend toward AI adoption in production workflows. Sarandos positioned the technology as a creative enhancement tool rather than just a cost-cutting measure, emphasizing AI’s potential to help creators produce “better” content alongside more affordable options.
This VFX application aligns with Netflix’s expanding AI initiatives, which already include conversational search features for content discovery and AI-powered ad integration that matches promotional content with show aesthetics. The company’s willingness to openly discuss these implementations suggests AI integration in entertainment production is moving from experimental phases toward standard industry practice.
Reflection AI Debuts Comprehensive Development Intelligence Platform
A new startup led by former Google DeepMind veterans has introduced an AI system that breaks from industry norms by treating software development as a holistic information ecosystem rather than a code generation problem.
Asimov, developed by Reflection AI, processes diverse data streams across development organizations—from version control repositories to team communications and project documentation—to build a contextual understanding of how software projects evolve. The approach contrasts sharply with current AI coding tools, which primarily focus on generating new code snippets.
The system architecture centers on what Reflection calls “deep research” methodology, deploying multiple information-gathering agents that feed findings to a central synthesis component. This design enables the platform to maintain institutional memory about development decisions, architectural choices, and team processes that typically exist only in scattered communications or individual knowledge.
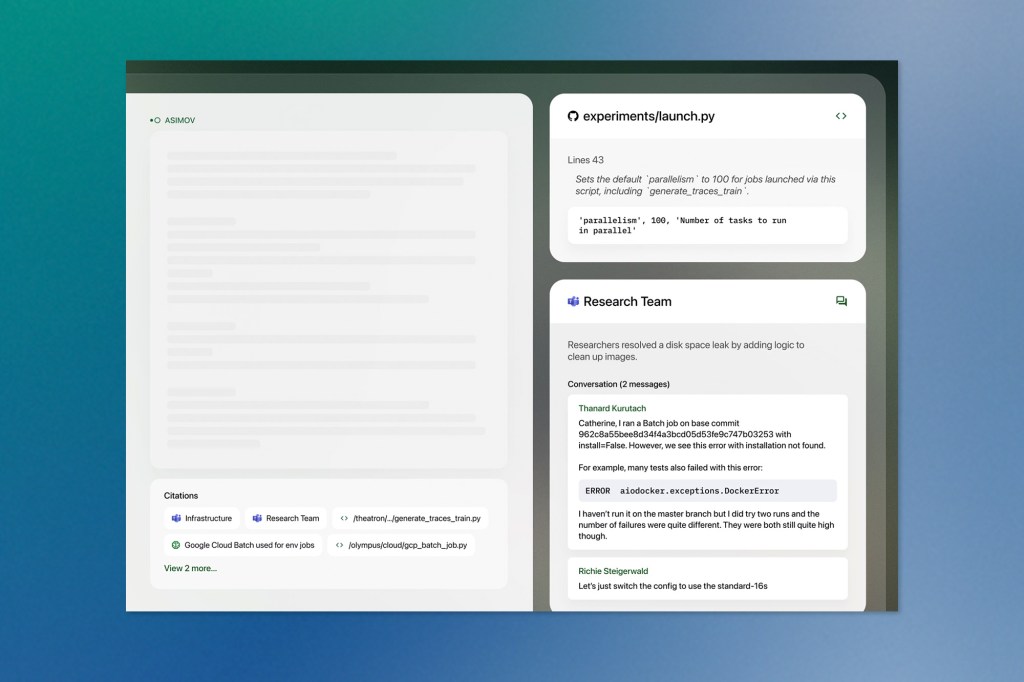
Central to the platform is a memory system allowing teams to explicitly store knowledge through natural language commands, with granular permission controls governing access and modification rights. This persistent knowledge base aims to capture the informal understanding that experienced developers accumulate about codebases and organizational practices.
Reflection’s founding team brings reinforcement learning expertise from breakthrough projects, such as AlphaGo, now applied to training models on software development workflows using both human feedback and synthetic data generation. The platform operates within customers’ private cloud infrastructure to maintain data sovereignty while accessing sensitive development communications.
Early testing suggests developers favour Asimov’s contextual responses over existing tools, with the company positioning this comprehensive approach as foundational for more advanced AI systems that could eventually understand and improve entire software development processes autonomously.
Google Tests Visual App-Building Tool for Non-Coders
Google has entered the increasingly competitive “vibe-coding” market with Opal, a new experimental tool that allows users to create web applications through natural language descriptions and visual workflows rather than traditional programming.
Available through Google Labs in the United States, Opal enables users to build mini web applications by simply describing what they want to create, with Google’s AI models handling the technical implementation. The platform features a gallery of existing applications that users can remix and modify, thereby lowering the barrier to experimentation and learning.
What distinguishes Opal from Google’s existing AI Studio is its visual workflow interface, which displays the input, output, and generation steps as an interactive diagram. Users can click on individual workflow components to examine and edit the underlying prompts that drive each process, or manually add new steps using Opal’s toolbar. This visual approach suggests Google is targeting a broader audience beyond developers who might find traditional coding interfaces intimidating.
The tool allows users to publish their creations directly to the web and share links for testing with others using Google accounts, creating a social element around app creation and iteration.
Google’s entry into this space intensifies competition in the rapidly growing no-code AI application market, joining established players like Canva, Figma, and Replit who are all developing tools to democratize app creation. The “vibe-coding” sector has attracted significant investor attention, with startups like Lovable and Cursor reportedly fielding acquisition offers as demand for accessible development tools continues to surge.
Majority of US Teens Engage with AI Chatbot Companions
A comprehensive study by Common Sense Media reveals that AI companion usage has reached significant penetration among American teenagers, with nearly three-quarters having experimented with conversational AI technologies designed for personal interaction.
The research, conducted with over 1,000 teens aged 13-17 during spring 2025, found that 72% have tried AI companions at least once, while 52% consider themselves regular users. Among frequent users, daily engagement reaches 13%, with 21% interacting several times a week. The study distinguished between AI companions—chatbots designed for personal conversation—and functional AI tools used for homework or information queries.
Teen motivations for using an AI companion span entertainment (30%), technological curiosity (28%), seeking advice (18%), and appreciating constant availability (17%). However, trust levels remain mixed, with half of the respondents expressing skepticism about information provided by these systems. Older teenagers demonstrate greater skepticism than their younger counterparts, suggesting that developing digital literacy occurs with age.
Notably, 39% of teens report using AI conversations as training grounds for real-world social interactions, practicing everything from basic social skills to emotional expression. While one-third find AI conversations more satisfying than human interactions, the majority still prefer real relationships. Encouragingly, 80% of AI companion users report spending more time with human friends than with chatbots, suggesting these tools supplement rather than replace human connection.
The findings arrive amid growing concerns about AI’s impact on teen mental health, including ongoing litigation involving Character.AI and questions about AI’s role in therapeutic contexts. This data provides a crucial baseline understanding of how young people integrate AI companions into their social and emotional development.
Keep ahead of the curve – join our community today!
Follow us for the latest discoveries, innovations, and discussions that shape the world of artificial intelligence.