Forget theoretical AI capabilities. The market has suddenly delivered tools that solve actual problems professionals face daily. Openai’s GitHub connector finally lets developers have meaningful conversations with their codebases. FutureHouse brings AI assistance directly to scientists with specialized tools that understand research literature and experimental design. Google has created a unique investment model that gives startups privileged access to DeepMind technology without restrictive cohort programs. Perhaps most ingenious is Gravatar’s transformation from a simple avatar service to a portable AI personalization layer. These innovations represent a turning point where AI moves beyond generic chat interfaces toward specialized tools that integrate seamlessly into professional workflows.
Listen to AI Knowledge Stream
AI Knowledge Stream is an AI-generated podcast based on our editor team’s “AI This Week” posts. We leverage cutting-edge AI tools, including Google Notebook LM, Descript, and Elevenlabs, to transform written content into an engaging audio experience. While AI-powered, our team oversees the process to ensure quality and accuracy. We value your feedback! Let us know how we can improve to better meet your needs.
OpenAI Connects ChatGPT’s Deep Research Tool to GitHub for Code Analysis
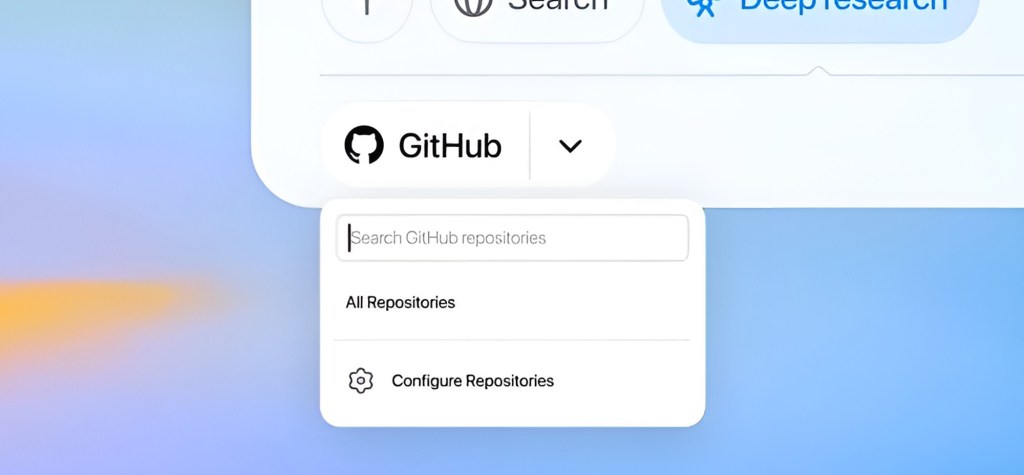
OpenAI has expanded its AI-powered “deep research” feature with a new GitHub connector, marking the tool’s first integration of this kind. This addition lets developers ask questions about codebases and engineering documentation stored on GitHub.
The GitHub connector represents a significant enhancement to ChatGPT’s deep research capabilities, which already allow users to search across the web and compile comprehensive research reports. This new functionality will be rolled out gradually, with ChatGPT Plus, Pro, and Team users gaining access over the next few days. Enterprise and Education users will receive the feature later, according to OpenAI.
Expanding AI Utility Through Platform Connections
This move aligns with the broader industry trend of AI companies creating connections between their chatbots and external platforms. While OpenAI previously offered plug-in capabilities for ChatGPT before pivoting to custom GPTs, this connector approach appears to be a new strategy for expanding functionality.
Practical Applications for Developers
The GitHub connector enables several valuable workflows for developers:
– Answering specific questions about codebases
– Breaking down product specifications into technical tasks and dependencies
– Summarizing code structure and patterns
– Understanding how to implement new APIs using real code examples
OpenAI emphasizes that the tool respects organizational access controls, ensuring users only see GitHub content they already have permission to view and repositories explicitly shared with ChatGPT.
OpenAI’s Continued Focus on Developer Tools
This GitHub integration is part of OpenAI’s broader investment in developer-focused capabilities. The company recently unveiled an open-source coding tool called Codex CLI and enhanced the ChatGPT desktop app to read code in several developer applications.
The company’s commitment to the programming space is further evidenced by reports of a potential $3 billion acquisition of Windsurf, an AI-powered coding assistant.
Additional Developments: Model Fine-Tuning Options
Alongside the GitHub connector announcement, OpenAI has introduced fine-tuning options for developers working with its newer models. Organizations can now customize the o4-mini “reasoning” model using a technique called reinforcement fine-tuning, which uses task-specific grading to improve model performance. Fine-tuning has also been made available for the GPT-4.1 nano model.
Access to these features varies, with o4-mini fine-tuning limited to verified organizations, while GPT-4.1 nano fine-tuning is available to all paying developers. This tiered access approach reflects OpenAI’s April decision to gate certain models and features behind verification requirements, which the company states is necessary to prevent potential misuse.
FutureHouse Debuts AI Tools Aimed at Accelerating Scientific Discovery
FutureHouse, an Eric Schmidt-backed nonprofit with the ambitious goal of building an “AI scientist” within the next decade, has launched its first major product offering. The organization unveiled a new platform and API featuring AI-powered tools specifically designed to support scientific research and discovery.
Four Specialized Research Tools
FutureHouse’s release consists of four distinct AI tools, each serving a different scientific workflow:
1. Crow – Searches scientific literature and answers questions about the findings
2. Falcon – Conducts deeper literature searches across scientific databases
3. Owl – Identifies previous work in specific subject areas
4. Phoenix – Assists in planning chemistry experiments using specialized tools
According to FutureHouse, these AI systems differentiate themselves through access to “a vast corpus of high-quality open-access papers and specialized scientific tools,” along with transparent reasoning processes that examine sources in greater depth than competing systems.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the organization’s claims about accelerating scientific discovery, FutureHouse has yet to achieve a scientific breakthrough or novel discovery using its AI tools. This highlights one of the fundamental challenges in developing an “AI scientist” – the unpredictable nature of scientific innovation.
While AI may excel at tasks requiring broad exploration, such as narrowing down possibilities from vast datasets, its capacity for the creative, out-of-the-box thinking that drives scientific breakthroughs remains unproven. FutureHouse itself acknowledges potential limitations, particularly with its Phoenix tool, noting that the systems “may make mistakes” and encouraging user feedback to improve functionality.
The nonprofit’s release comes amid intense competition in the scientific AI space, with numerous startups and established tech companies developing similar tools, often backed by significant venture capital. Earlier this year, Google introduced its “AI co-scientist,” a tool designed to help researchers create hypotheses and experimental research plans.
Google Launches AI Futures Fund to Support DeepMind-Powered Startups
Google has announced the creation of the AI Futures Fund, a new initiative designed to invest in startups building with Google DeepMind’s AI tools. Launched on May 12, 2025, this program aims to nurture companies leveraging Google’s AI research and development capabilities across various funding stages.

Unlike traditional accelerator programs, the AI Futures Fund operates on a rolling basis without fixed application windows or cohorts. The initiative will provide multi-faceted support to selected startups, including:
– Early access to Google DeepMind’s AI models
– Collaboration opportunities with experts from DeepMind and Google Labs
– Google Cloud credits to support infrastructure needs
– Potential direct investment from Google
Early Participants and Application Process
The program has already engaged with early participants, including meme-creation platform Viggle and webtoon app Toonsutra. Interested startups can now apply for consideration, though Google has not disclosed the fund’s total size or typical investment amounts. The company indicates that check sizes will vary based on each startup’s stage and specific needs, with a focus primarily on early to mid-stage companies while maintaining flexibility for later-stage opportunities.
Gravatar Introduces AI Profile Builder for Personalized AI Interactions
Gravatar has launched a new AI Profile Builder tool that transforms its long-standing digital avatar service into an AI identity platform. Announced on May 6, 2025, this tool allows users to create portable profiles of their preferences, interests, and background information that can be seamlessly shared across AI systems.
The company positions this new offering as an extension of Gravatar’s original purpose as a “digital business card for the web,” now evolved to serve as a personal identity layer for artificial intelligence interactions.

How the AI Profile Builder Works
The new system allows users to create standardized profiles that AI tools can easily interpret:
1. Users complete their Gravatar profile with personal information
2. They set communication preferences including preferred tone, depth, and humor
3. The system generates a portable markdown file containing the profile
4. Users can paste this profile into various AI tools for personalized experiences
This approach aims to eliminate the need for users to repeatedly train different AI systems on their preferences, creating a “build once, use everywhere” solution for AI personalization.
Practical Applications
Gravatar demonstrates several use cases for this technology, including PDF completion assistance and personalized daily briefings. The company highlights how the system can transform generic AI responses into personalized ones by incorporating hobbies and interests, location-based recommendations, and more.
Developer Integration
For developers looking to incorporate this functionality, Gravatar offers simple integration options. Applications can access user profiles through a markdown request, REST API, or mobile SDKs. The basic implementation requires minimal code, with profiles available at a straightforward endpoint:
https://gravatar.com/{EmailHash}.mdThe company emphasizes that this service remains free to use as “part of the open web.”
Privacy and Control Emphasis
Gravatar positions its approach as a transparent alternative to “black-box AI systems that build hidden profiles,” emphasizing user control over how personal information is shared with AI systems. The solution allows users to maintain consistent personalization across services while retaining authority over their digital identity.
This initiative represents a strategic pivot for Gravatar, leveraging its established position as a digital identity provider to address emerging needs in the AI ecosystem.
Keep ahead of the curve – join our community today!
Follow us for the latest discoveries, innovations, and discussions that shape the world of artificial intelligence.