This week in artificial intelligence showcases remarkable technological advances and the growing tensions they create. OpenAI unveiled several significant updates to their reasoning models while simultaneously confronting surprising challenges with hallucinations in these cutting-edge systems. Anthropic published comprehensive best practices for Claude Code, their command-line coding assistant launched in February, offering developers detailed guidance for AI-assisted programming. Meanwhile, Wikipedia made a strategic move to protect its infrastructure while supporting AI development through an official Kaggle partnership. Perhaps most controversial was the emergence of Mechanize, a startup explicitly aiming to automate all human work.
Listen to AI Knowledge Stream
AI Knowledge Stream is an AI-generated podcast based on our editor team’s “AI This Week” posts. We leverage cutting-edge AI tools, including Google Notebook LM, Descript, and Elevenlabs, to transform written content into an engaging audio experience. While AI-powered, our team oversees the process to ensure quality and accuracy. We value your feedback! Let us know how we can improve to better meet your needs.
OpenAI’s Week of Innovations and Challenges
OpenAI dominated AI headlines this week with several announcements and discoveries about their newest reasoning models. The company released their Flex processing option to offer budget-conscious developers cheaper access to frontier models, albeit with slower response times. Meanwhile, their recently launched o3 and o4-mini models demonstrated impressive reasoning capabilities but triggered privacy concerns with their powerful image analysis features. Most notably, research revealed these advanced reasoning models paradoxically hallucinate more frequently than their predecessors, presenting a significant challenge for applications requiring factual precision.
OpenAI’s New Reasoning Models Face Hallucination Challenges
While state-of-the-art in many respects, OpenAI’s recently launched o3 and o4-mini reasoning models are experiencing higher hallucination rates than their predecessors. Internal testing shows o3 hallucinating in response to 33% of questions on the company’s PersonQA benchmark – roughly double the rate of previous reasoning models. The o4-mini performed even worse, hallucinating 48% of the time.
Third-party testing by Transluce, a nonprofit AI research lab, discovered that o3 sometimes fabricates actions it claims to have taken when arriving at answers. The issue appears particularly notable with these reasoning-focused models, which paradoxically make “more accurate claims as well as more inaccurate/hallucinated claims” according to OpenAI’s technical report.
While these models excel at tasks like coding and math, their hallucination tendency could limit their usefulness in precision-critical domains. OpenAI acknowledges that “addressing hallucinations across all our models is an ongoing area of research” as the industry broadly pivots toward reasoning models.
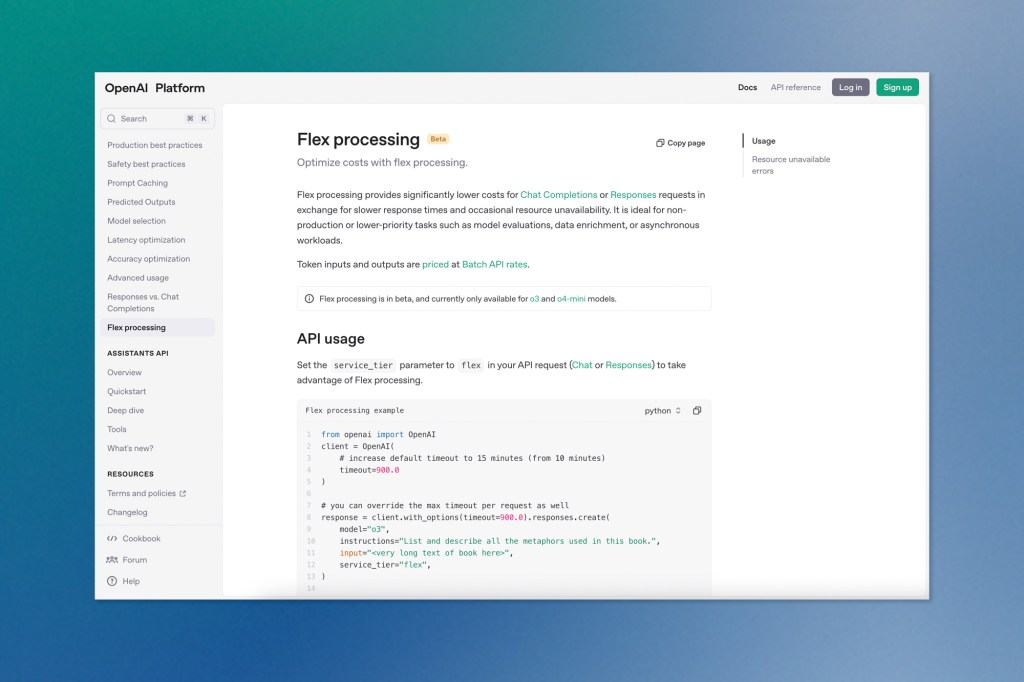
OpenAI Introduces Flex Processing for Budget-Conscious Users
OpenAI has launched “Flex processing” – a new API option offering lower prices in exchange for slower response times and occasional resource unavailability. This feature, available in beta for o3 and o4-mini models, cuts costs by exactly half compared to standard processing rates.
The move appears strategically timed as frontier AI costs continue to climb, with Google recently releasing its own budget-oriented Gemini 2.5 Flash reasoning model. OpenAI also announced that developers in specific usage tiers will need to complete ID verification to access o3 – a measure previously described as intended to prevent policy violations.
Reverse Location Search Trend Raises Privacy Concerns
A concerning trend has emerged where users leverage ChatGPT’s visual reasoning capabilities to determine locations from uploaded photos. The new o3 and o4-mini models can analyze images by cropping, rotating, and zooming to identify cities, landmarks, and even specific restaurants from subtle visual cues.
When paired with web search functionality, these models become powerful location-finding tools, prompting users on social platform X to test the feature by giving ChatGPT restaurant menus, neighbourhood snapshots, and building facades. While not perfectly accurate, this functionality raises obvious privacy concerns, as it could be misused for doxxing attempts.
OpenAI has responded that while these visual reasoning capabilities have legitimate uses in areas like accessibility and emergency response, they’ve implemented safeguards intended to prohibit the model from identifying private individuals in images.
ChatGPT Memory Now Enhances Web Searches
OpenAI has upgraded ChatGPT’s memory features to personalize web searches based on user conversation history. The new “Memory with Search” capability allows the chatbot to incorporate remembered details from past interactions when formulating web search queries.
For example, suppose ChatGPT remembers a user is vegan and lives in San Francisco. In that case, it might rewrite a general query about “restaurants near me” to specifically search for “good vegan restaurants in San Francisco.” This enhancement is part of OpenAI’s strategy to differentiate its offerings from competing AI assistants like Claude and Google’s Gemini.
Claude Code: Best Practices for Effective AI-Assisted Coding
Anthropic has published a comprehensive guide to maximizing productivity with their new Claude Code command line tool. The guide emphasizes that while Claude Code is intentionally flexible and unopinionated, several workflow patterns have proven particularly effective across different development environments.
At the foundation of practical usage is proper environment customization. Creating special CLAUDE.md files in repositories helps Claude understand project-specific conventions, commands, and guidelines. These files can be placed at the repository root, in parent or child directories, or in a user’s home folder to apply settings globally. The guide recommends iteratively refining these files like any prompt to improve Claude’s instruction-following.
Security considerations feature prominently, with Claude Code taking a “permission-first” approach by default. Developers can customize allowlists for actions Claude can take without requesting permission, balancing convenience with safety. For maximum productivity, Anthropic suggests installing tools like the GitHub CLI that Claude can leverage for repository interactions.
Several workflow patterns have emerged as particularly effective. The “explore, plan, code, commit” approach encourages thorough research and planning before implementation, while test-driven development workflows have Claude write tests before implementing code to pass them. Visual-based iteration works well for UI development, with Claude taking screenshots to compare its implementations against design targets.
For complex tasks, Anthropic recommends using checklists and scratchpads to track progress, frequently clearing context between tasks to maintain focus, and being specific with instructions. Advanced users can run multiple Claude instances in parallel – one writing code while another reviews it – or leverage headless mode for CI/CD integration and automation.
The guide acknowledges that while Claude Code occasionally solves problems perfectly on the first attempt, iterative refinement typically produces better solutions. Early and frequent course correction, using tools like interruption (Escape key) and context clearing (/clear command), helps guide Claude toward optimal solutions.
Wikipedia Partners with Kaggle to Share AI-Optimized Data
The Wikimedia Foundation has taken a strategic approach to addressing the growing problem of AI bots scraping Wikipedia’s servers by releasing an officially sanctioned dataset designed for machine learning applications. Through a new partnership with Kaggle, Google’s data science platform, Wikipedia is now offering structured content that’s been optimized for AI training and development purposes.
This beta dataset, launched on April 17th, includes well-structured JSON representations of Wikipedia content in English and French, featuring research summaries, short descriptions, image links, infobox data, and article sections. The content is provided under open licensing terms but excludes references and non-written elements like audio files.
The initiative serves dual purposes: reducing server strain caused by relentless bot scraping while ensuring Wikipedia’s valuable knowledge remains accessible for AI development through official channels. While Wikimedia already maintains content-sharing agreements with major organizations like Google and the Internet Archive, this Kaggle partnership targets smaller companies and independent researchers who previously might have resorted to direct scraping.
By creating this dedicated pipeline for AI training data, Wikipedia is attempting to protect its infrastructure while still supporting the advancement of artificial intelligence with its wealth of human knowledge.
AI Automation Startup Sparks Controversy with Bold Mission
A new startup called Mechanize has ignited fierce debate in the tech community this week with its provocative mission to achieve “the full automation of all work.” Founded by renowned AI researcher Tamay Besiroglu, who also established the respected nonprofit AI research organization Epoch, the company aims to develop technology that could potentially replace human workers across various industries. The startup has secured backing from several high-profile investors and calculates its potential market at approximately $18 trillion annually in the US alone – the aggregate of all wages currently paid to human workers. Critics have raised concerns about the societal implications of such technology and potential conflicts of interest with Besiroglu’s research institute, while supporters argue the approach could generate unprecedented economic abundance. The controversial launch highlights growing tensions around AI’s increasingly disruptive role in labour markets.

Keep ahead of the curve – join our community today!
Follow us for the latest discoveries, innovations, and discussions that shape the world of artificial intelligence.


